Parts of a Sentence Worksheets
Can you recognize a subject, object,
predicate, and complement in an English sentence? Get some review and
practice with these parts of a sentence worksheets!
You'll need to feel comfortable with how a sentence is constructed if you want to improve your writing and speaking. These worksheets contain illustrations and examples, as well as exercises and an answer key so that you can practice the skills.
Click Here for Step-by-Step Rules, Stories and Exercises to Practice All English Tenses
You'll need to feel comfortable with how a sentence is constructed if you want to improve your writing and speaking. These worksheets contain illustrations and examples, as well as exercises and an answer key so that you can practice the skills.
Can you find the subject and the predicate in an English sentence? Do you remember the difference between transitive and intransitive verbs? How about the difference between objects and complements?
It sounds like a lot to keep in mind, but it's really not complicated. First, we'll have a quick review of the different parts of English sentences, and then you can practice these skills with the exercises.
For full, illustrated explanations of all these topics, review the English parts of a sentence article.
Let's start with our quick review.
Subject
To make a sentence in English, we need two basic parts: a subject and a verb.The subject of an English sentence is the person or thing that performs the action, or that the sentence makes a statement about.
For example:

- Maggie screams.
In this sentence, Maggie is the person performing the action. What does Maggie do? She screams.
- The cat is scared!
In this sentence, the cat performs the action. How does the cat feel? It is scared.
Remember that a subject can be a noun, a pronoun, or a noun phrase.
Predicate
The predicate is the statement that is made about the subject. It contains at least one verb and can have more words that give more information about the subject.Be sure to review the article on predicates for a full explanation.
For example:

- Fred is jumping happily through his house.
Now, what about Fred? He is jumping happily through his house. This is a simple predicate because it contains one verb. Remember that a simple predicate can have lots of other words that give more information!
- Fred is jumping, laughing, and singing.
Objects and transitive and intransitive verbs
In English, there are two kinds of verbs: transitive and intransitive. Those names might sound confusing, but it's really very simple.Transitive verbs take objects. This means that the action of the verb affects something else. The person or thing that the verb affects in some way is an object.
For example:

- Gerald baked some cookies!
What did Gerald bake? He baked some cookies. The cookies were directly affected by his action. They were baked!
Because the cookies were directly affected by Gerald's action, they are the direct object of the transitive verb "baked."
Now, let's imagine that Gerald had someone special in mind when he baked those cookies.
- Gerald baked his friends some cookies.
The indirect object comes between the verb and the direct object, like in the example above.
| subject + verb + indirect object + direct object |
Now, there's only one more kind of object: the object of the preposition. These objects are very easy to identify because they always come right after a preposition.
- Gerald baked some cookies for his friends.
Complements and linking verbs
There is a special group of verbs in English called linking verbs. They are very common and let us give more information about the subject with an adjective or a noun that describes it.So, this adjective or noun (or adjective phrase or noun phrase) is the complement! It gives more information about the subject and always follows a linking verb.
Be sure to review the articles on complements for full, illustrated explanations.
For example:

- Jill is a bus driver.
- She looks happy.
- She becomes sleepy after she reads.
So, those are the basic parts of an English sentence! Now, let's get some practice with the exercises.
Exercise A: Subjects and predicates
Complete the subjects under each picture with the predicates from the table to form a complete sentence.Predicates:
| won't have time to finish all those dishes before the guests arrive! |
| is having a conversation at the office. |
| really has a very mess closet! |
| ran because he was in a big hurry. |
| forgot to put on his trousers this morning! |
Subjects:
1.

The group of men ____________________
2.

Jimmy ____________________
3.

Marie ____________________
4.

Mr. Fredrickson ____________________
5.

Craig ____________________
Exercise B: Direct objects
Underline the direct object in the following sentences.1.

Dr. Rodriguez gave his patient advice.
2.

The man is holding the red block.
3.

They are singing a song for their audience.
4.

He is carrying a heavy bag of mail today!
5.
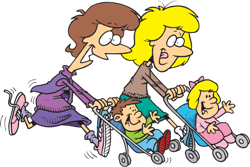
The mothers are pushing their children in the park.
Exercise C: Indirect objects
Complete the sentences below by adding the indirect object in the correct place in each sentence. The indirect object is in parentheses () after the sentence.1.

He is giving some good news! (his sister)
2.

He is making dinner. (his children)
3.

Johnny is playing a blues song. (the audience)
4.

The little boy has told a joke. (them)
5.

My son painted a beautiful picture! (me)
Exercise D: The object of the preposition
Use the prepositions from the table to complete the sentences below. The object of the preposition is in bold.| to |
| between |
| on |
| for |
| into |
1.

Ted threw a party _____ his best friend.
2.

The tourist carried his bags _____ the hotel.
3.

Lily is afraid to step _____ the ice.
4.

He kicked his computer monitor _____ a big trash can.
5.
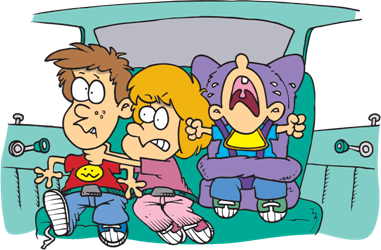
Penny has to sit _____ her brothers.
Exercise E: Linking verbs and complements
Match the correct complements from Table B with the subjects and linking verbs from Table A. Use the pictures in Table A to help.Table A: Subjects and linking verbs
1. The mother and her little baby seem |
2. That garbage smells |
3. In the evening, Geoff becomes  |
4. The boy looks |
5. Peter is 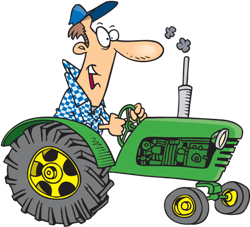 |
Table B: Complements
| a. sad. |
| b. very happy! |
| c. a farmer. |
| d. terrible. |
| e. tired. |
Answer Key
Exercise A: Subjects and predicates1. The group of men is having a conversation at the office.
2. Jimmy ran because he was in a big hurry.
3. Marie won't have time to finish all those dishes before the guests arrive!
4. Mr. Fredrickson forgot to put on his trousers this morning!
5. Craig really has a very mess closet!
Exercise B: Direct objects
1. Dr. Rodriguez gave his patient advice.
2. The man is holding the red block.
3. They are singing a song for their audience.
4. He is carrying a heavy bag of mail today!
5. The mothers are pushing their children in the park.
Exercise C: Indirect objects
1. He is giving his sister some good news!
2. He is making his children dinner.
3. Johnny is playing the audience a blues song.
4. The little boy has told them a joke.
5. My son painted me a beautiful picture!
Exercise D: The object of the preposition
1. Ted threw a party for his best friend.
2. The tourist carried his bags to the hotel.
3. Lily is afraid to step on the ice.
4. He kicked his computer monitor into a big trash can.
5. Penny has to sit between her brothers.
Exercise E: Linking verbs and complements
1. The mother and her little baby seem very happy.
2. That garbage smells terrible.
3. In the evening, Geoff becomes tired.
4. The boy looks sad.
5. Peter is a farmer.
Get Updates, Special Offers, and English Resources
Download your FREE GIFT (the first two chapters of
English Short Stories Book and Workbook)
as soon as you join!

By submitting your email, you consent to receiving updates and newsletters from us and to the sharing of your personal data with third parties for the purposes of sending you communications. We will not spam you. You can unsubscribe at any time. For more information, please see our privacy policy.
Return
from Parts of a Sentence Worksheets to English Parts of a Sentence
Return to
Really Learn
English Home Page





